Corundum  |
Quick Links: |
Basic Data on Corundum
| COMPOSITION |
Al2O3 |
| HARDNESS |
9 (1/400 the hardness of a diamond) |
| CRYSTAL SYSTEM |
Hexagonal* |
| INCLUSIONS |
Common (minerals and glass) |
| SPECIFIC
GRAVITY |
High (around 4.0) |
*Note: some texts list the crystal system of ruby as trigonal. Trigonal
is more simply considered a subdivision of the hexagonal crystal system.
| COLOR |
Red (ruby is Latin for red), may also be pinkish or brownish-red; |
|
(absorbs blue, transmits and fluoresces red) |
| PLEOCHROISM |
Strong |
| IMPURITIES |
Red: Cr+++ (< 1%), Brown: Fe+++ |
Physical characteristics: composition, structure etc. same as for a ruby.
Color
(other than ruby red) 
The blue color is due to charge transfer involving Fe-Ti (see
lecture on color
in minerals for details!.
Different concentrations of various impurities produce a range
of colors from quite
pale, due to low concentrations, to quite
deep blue. Other colors include:
purple
and pink,
yellow, orange, green, etc.
|
What is corundum?
Where is corundum formed and found?
How are crystals cut?
Star rubies and sapphires
Natural versus synthetic?
Treatments
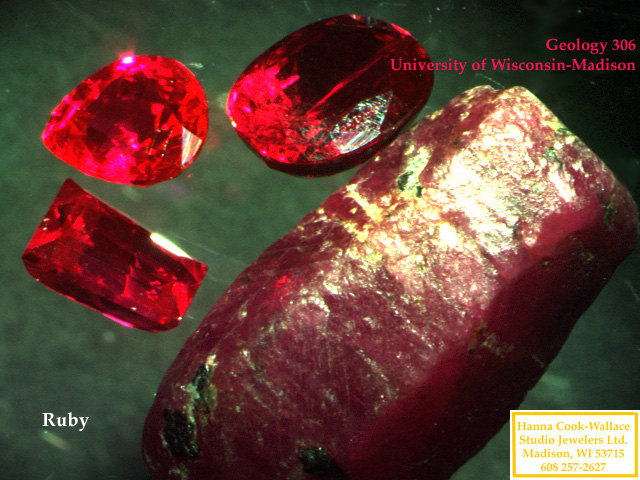


|
Origin of Rubies and Sapphires (Corundum):
Rubies and sapphires are found in Burma, Thailand, Sri Lanka |
|
Cutting:
Cutting refers to the proportions and finish of a gem, regardless of the
shape or size. In other words, did the cutter do a good job? Are the facets
(polished faces) placed symmetrically? Are they smooth, or do they have
minute pits and lines? Are the facet junctions crisp, and do the facets
meet correctly? Is the pavillion (the bottom) of the stone of sufficient
depth that you see bright reflections across the entire face of the stone?
A stone that is shallow "leaks" light out the bottom and is not brilliant.
This is called "windowing"--you can see right through the stone, like through
a window.
More details on the importance of refractive index and critical angle
are provided in the first
lecture
Crystals normally cut with table of cabochon perpendicular to long axis
of crystal (long axis is axis about which crystal has hexagonal symmetry)
results in best color (because it is pleochroic).
-
normally use a mixed cut on the crown
-
brilliant and step cut on the pavillion
|
|
Clarity:
Undesirable inclusions
While many cut rubies and sapphires contain inclusions, gems that have
eye-visible inclusions are less desirable than "eye-clean" stones. In some
cases, inclusions can make the stone more vulnerable to breakage.
 Desirable
inclusions: Desirable
inclusions:
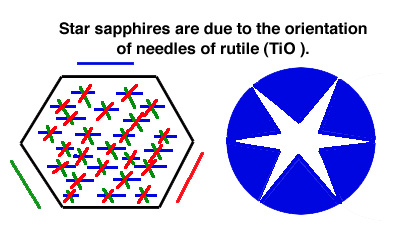
Give rise to asterism (star stones): 'silk'-like texture due to fine
rutile needles throughout the crystal. The light reflects from
the fibers -> 6-
pointed star.
NOTE: There are 3 special orientations in which rutile crystals occur.
These are parallel to hexagonal faces and thus at 60 degrees. Note
that the chemical formula of rutile is TiO2, and Ti is one of the elements
responsible for color in some sapphires.
Another example of a star
Ruby
|

|
Natural
versus synthetic
Rubies
and
sapphire are commonly synthesized
by the Verneuil
method
It is possible to synthesize both clear crystals and stars. The first
synthetic rubies appeared on the market in 1908.
Usually, a single crystal or boule
is grown from a melt by one of several
methods.
How do I tell if the stone is synthetic?
Natural origin may be proved by inclusions (e.g., natural gaseous
and fluid bubbles) and spectroscopic measurements.
Synthetic origin may be indicated by
-
the presence of flux inclusions and non-natural gas inclusions
-
synthetic corundum may contain a visible seed crystal (esp. in older gems)
-
whispy white veils
-
strain cracks, curved striae etc...
|
 An example of a
synthetically created ruby. |
| Treatments:
Heat Treatment of Corundum
Heat treatment of gemstones to is done to improve their appearance.
Heat treatment may change the color of corundum for a variety of reasons.
In some cases, heating the stone causes changes in the oxidation state
of impurites. An especially important example involves reduction of Fe
(conversion of Fe+++ to Fe++). Fe++ causes color in a variety of sapphires
via charge transfer (see lecture on color
in minerals).
Conversely, stones that are too deeply blue may be lightened by oxidation
of Fe (converstion of Fe++ to Fe+++)
In some cases, heat treatment will improve the depth of color because
heat causes dissolution of inclusions and diffusion of impurites (especially
Ti from rutile inclusions) into the surrounding corundum. Because fine
inclusions cause some stones to look cloudy, heat treatment that dissolves
the inclusions may also improve the clarity of the stone.
Heat treatment may also remove local color concentrations (remove patches
of color) because heat allows the color-causing impurity (Cr, in the case
of ruby) to more evenly distribute through the crystal. (however, this
may require such long times that it is impractical)
The conditions for heat treatment vary, depending upon the individual
stone. Some typical values and conditions are listed here
How do I tell if a stone has been heat treated?
Detection of heat and diffusion treatment is possible because
these treatments modify natural inclusions. This may involve rupture of
gas or fluid inclusions or partial dissolution of mineral inclusions. For
gems that contained needles, the needle margins may become diffuse.
Themelis states that "glass-appearing" inclusions may be found on rubies
that have been heat-treated with borax-based substances.
|
|
Diffusion Treatment of Corundum
Why? Color enhancement can be achieved through
addition of the color-causing impurity to the surface of the faceted gemstone.
For Ruby, this involves heating the stone to very close to its melting
point in the presence of a chromium source (chromium oxide powder: Cr2O3).
Chromium enters into the structure of the corundum (diffuses into the corundum).
This is a slow process, so chromium enrichment only occurs in the surface
layer. This is sufficient to produce a strong color enhancement that is
difficult to detect by eye.
Diffusion treatment for sapphires is similar to that for any corundum
variety. To enhance the blue color Fe and Ti oxide powders are placed in
contact with the faceted gem and Fe and Ti diffuse into the surface of
the stone.
Note that diffusion treatement is done to faceted stones and is probably
not obvious by
inspection under normal viewing conditions!!
Some specifics for conditions for sapphire and ruby treatments are given
in
this table.
How do I tell if a stone has been diffusion treated?
There are several ways you can determine if your stone has
been treated. Diffusion treatment will result in concentration of color
at facet junctions, and will modify the refractive index of the gemstone.
An excellent, simple, non-destructive method is as follows:
Place the faceted
gem in methylene
iodide. Note that color concentrations are apparent at facet junctions
(where the gemstone is thin). This color concentration tells us that the
deeply colored layer is quite thin!
This
is how these gemstones look under normal viewing conditions!
To demonstrate that the layer is thin, we polished
off
a part of the girdle region, exposing the pale, untreated interior.
|
|
| some
other comments and information |
|







 Desirable
inclusions:
Desirable
inclusions:
