Quartz & Zoisite |
Quick Links
Quartz Zoisite |
||||||||||||||
 |
What is quartz?
Varieties of quartz Where is it found? Synthesis Treatments |
||||||||||||||
What is Quartz?
Quartz has no cleavage and fails by brittle, conchoidal fracture; the fracture surfaces have vitreous luster. |

Quartz images. 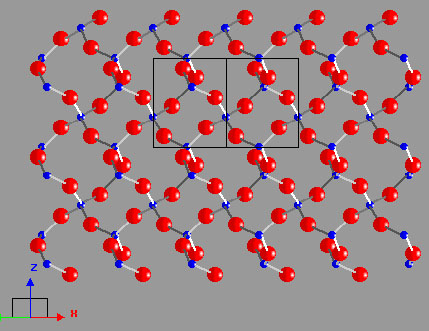
Movie showing quartz structure |
||||||||||||||
VarietiesSiO2 exists in several forms, the most common of which is low-temperature (alpha) quartz. |
 |
||||||||||||||
Quartz:
pure SiO2 is colorless, not normally used as a gem.
used in optical devices, etc. (like radio frequency oscilltors) can be doubly terminated |
 |
||||||||||||||
| Amethyst |  |
||||||||||||||
Citrine
the color is due to the presence of Fe, which is also the impurity present in amethyst. The term "ametrine" refers to bi-colored citrine/amethyst (junction is a peach color). |
 |
||||||||||||||
Smoky
quartz
if there is sufficient Al and radiation, the crystal can turn completely black! ("morian") Also sometimes faceted |
 |
||||||||||||||
Rose
quartz
the color is often due to the element Titanium (Ti) used for beads etc. sometimes you can find star rose quartz which has inclusions often massive (aggregates of crystals, not single crystals) |
 |
||||||||||||||
| Green
quartz
Milky quartz
often associated with gold deposits - used as a gem mainly if gold present |
|||||||||||||||
Rutilated
quartz is (normally) clear quartz that contains fine, often oriented,
rutile
crystals.
common in jewelry The term "venus hair" refers to fine red rutile needles Note the orientations of the rutile needles |
 |
||||||||||||||
Tourmaline and other inclusions
fine tourmaline needles a second example of green tourmaline in quartz other inclusions can involve minerals (possibly rutile) and open tubes, for example:
the three dimensional nature of these needles is quite apparent |
 |
||||||||||||||
Chatoyant quartz
due to the presence of needles of asbestos etc. Form when prexisting minerals are replaced by quartz ('fossilized')Other fibrous varieties, including agate and chrysophrase are discussed in later lectures Adventurine: green quartz containing platy inclusions of mica;
can be used as a substitute for jade; used in beads etc.
|
 |
||||||||||||||
| Quartz can also contain inclusions of trapped fluid that may contain
mineral precipitates and gas bubbles ('fluid
inclusions') [Note the bubble of liquid and gas in this image is round.
The black line is marker to draw your attention to the appropriate region).].
These tell us about the fluids present when the quartz formed. For example,
fluids may be quite saline, indicating quartz grew from salt-rich solutions.
|
 |
||||||||||||||
Where does it come from ?
|
|||||||||||||||
Synthesis
Doped quartz (quartz containing an impurity such as cobalt (Co) may be synthesized to achieve bright colored materials. |
 |
||||||||||||||
Heat Treatment: Citrine and amethyst:Primitive methods can be employed like using a wheelbarrow to immerse crystals in sand within a fire to heat them to a high enough temperature to modify the oxidation state of the Fe. |
|||||||||||||||
Quartz has some interesting propertiesPiezoelectricitysome other comments |
|||||||||||||||
Zoisite (Variety Tanzanite) |
What is it?
Where is it found? |
||||||||||||||
What is it ?
|

View some images of tanzanite |
||||||||||||||
Where is it found?
|
|||||||||||||||
Other:
|