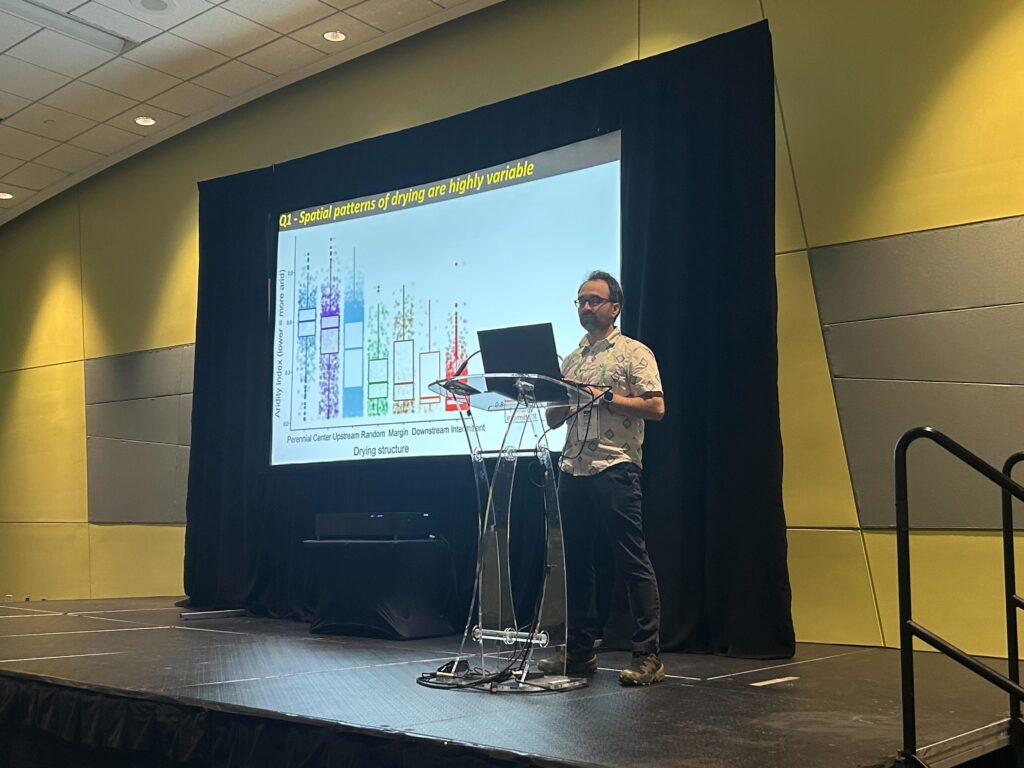
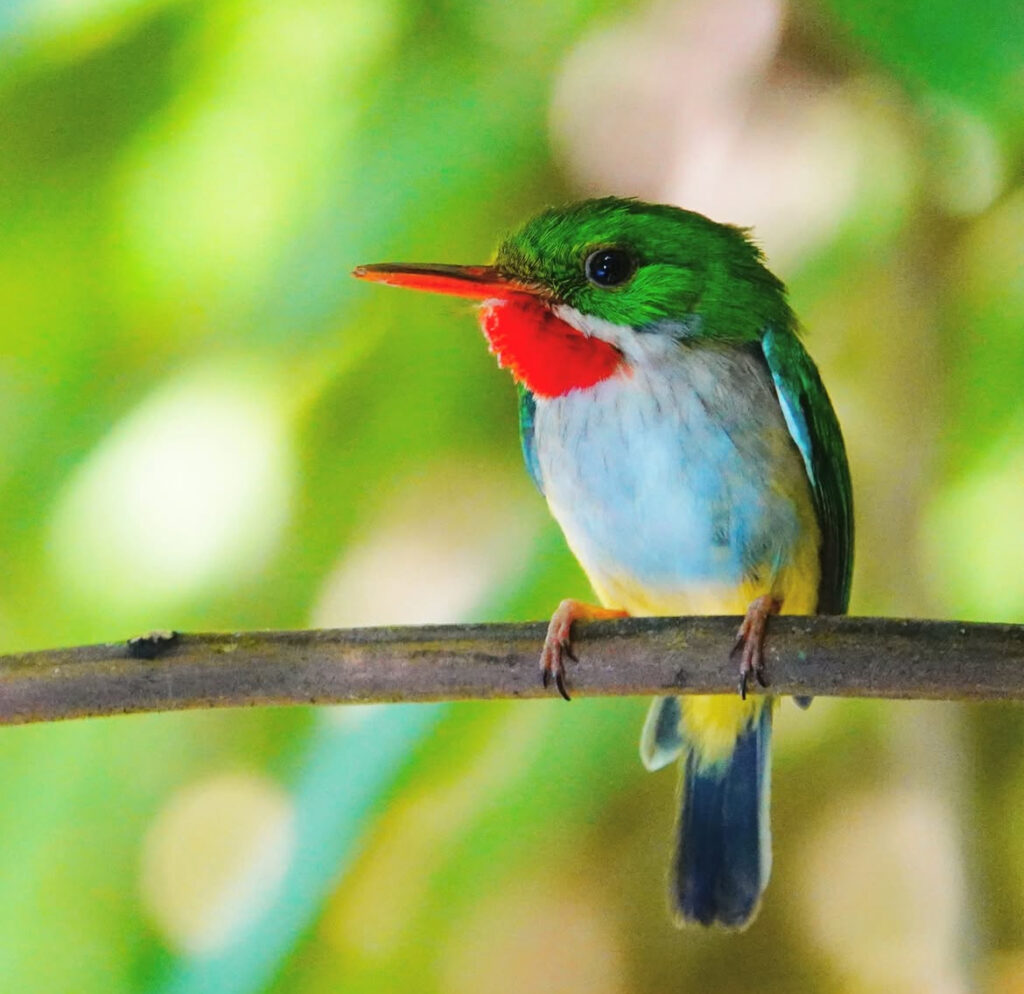
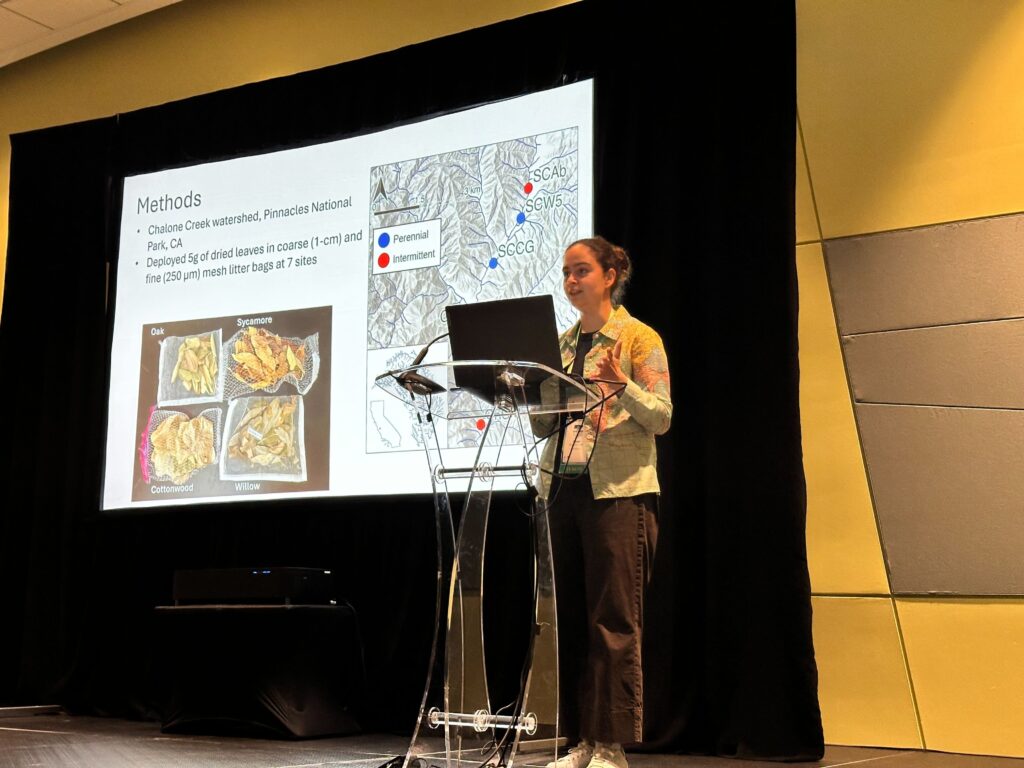
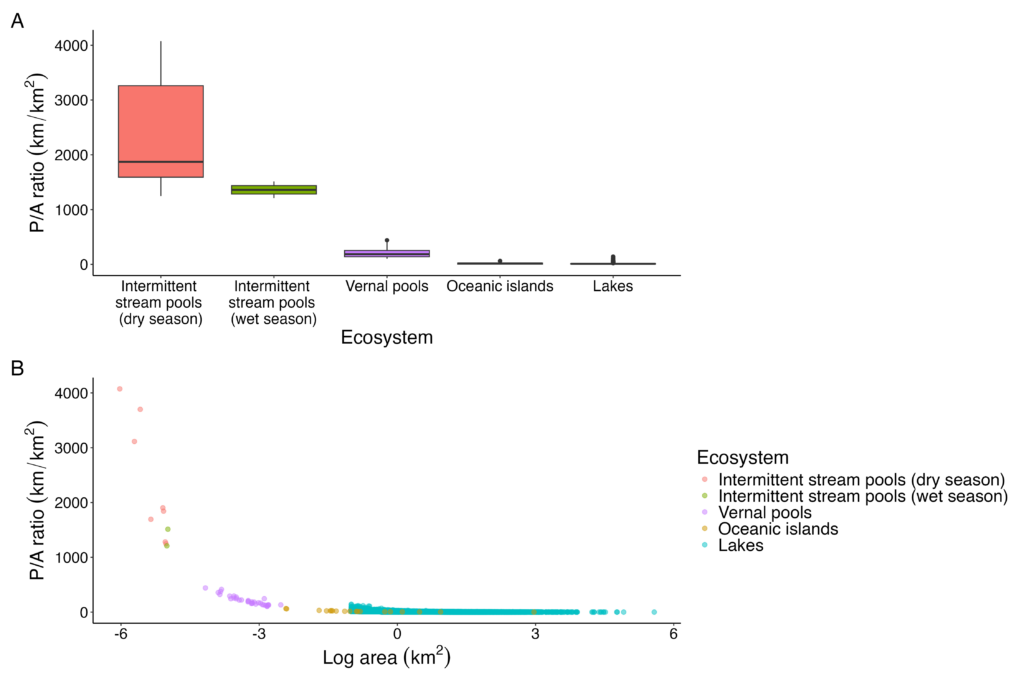
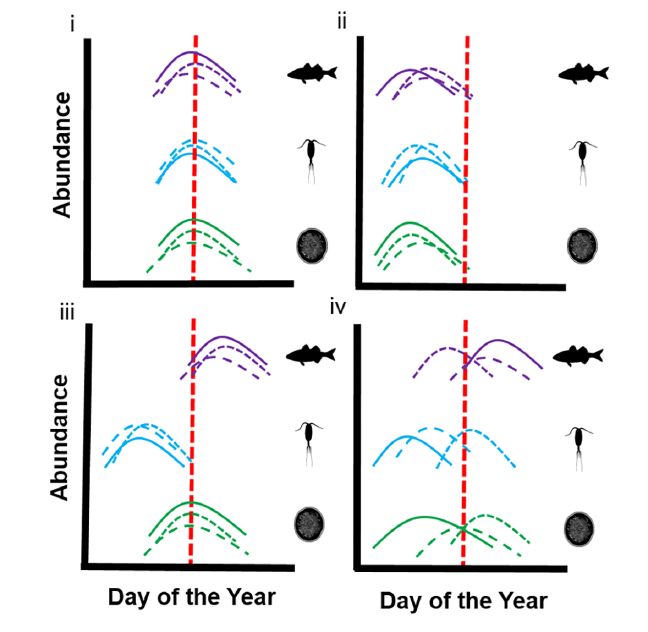
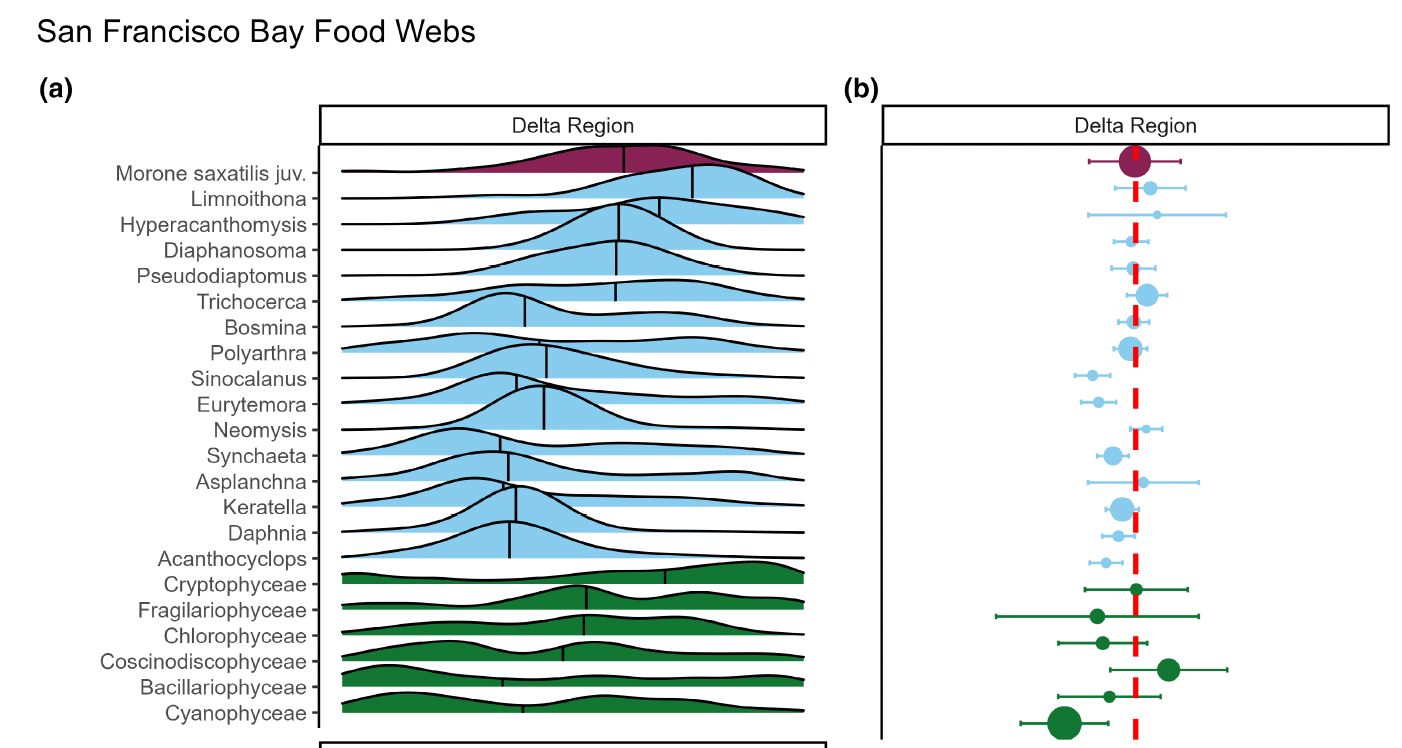
Albert and Rose attended the Society for Freshwater Science Annual Meeting in San Juan, Puerto Rico! Albert presented about how spatial patterns of river drying interact with fragmentation and disturbance to reduce biodiversity. Rose presented results from a leaf litter decomposition experiment where she found that lower leaf litter quality primarily explains slower breakdown rates at intermittent compared to perennial flow sites. They also fit in some time to hike and birdwatch in El Yunque National Forest, spotting the beautiful San Pedrito (Puerto Rican tody) and exploring creeks with freshwater shrimp!