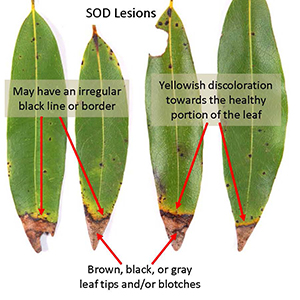
A tree’s Critical Root Zone (CRZ), sometimes also called the Root Protection Zone (RPZ), is defined as a circle on the ground corresponding to the dripline of the tree. Unfortunately the “dripline” of a tree can be irregular and hard to define. An alternative method of determining this dimension is to measure the diameter of the tree trunk in inches at breast height (DBH), multiplied by 12, as so:
Trunk diameter in inches at 4 1/2′ (1.4m) above grade x 12 = radius in feet of the CRZ (essentially, 1′ of CRZ radius per 1″ DBH or roughly 1.2m of CRZ per 10cm of DBH).
Bear in mind that root systems vary by depth and spread based on tree species, age, soil type, etc. The root systems of some oaks, for example, can extend well beyond the canopy dripline. This full root zone may extend 2 to 3 times beyond the CRZ.
Damage to the tree roots can be caused by any disturbance inside this area however bear in mind that nearby trenching, paving, or altering drainage patterns outside the immediate RPZ may also significantly affect the tree.