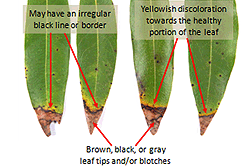
|
The traditional method for identifying Phytophthoras is to isolate and grow them on Petri plates containing a selective growth media.
|
|
|
|
Microscopic organisms are isolated from infected soil or plant tissue and sterile cultured on to Petri plates containing PARP agar. PDF |
|
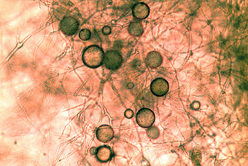
After 5 to 7 days the plates are examined under a microscope for the presence of the distinctive spores of Phytophthora ramorum.
|
|
Pros and Cons of the culturing method:Pro:
– Only relatively low tech equipment required.
– Culturing techniques are relatively easy to learn.
– Relatively low cost (although PARP media is expensive).
Con:
– State and Federal permits required to keep live P.ramorum cultures.
– Cultures from infected material do not always grow on agar media.
– May provide false negative results.
Jump to Other SOD Diagnostic Methods:
Immunostrips – Culturing – EIA Analysis – PCR Analysis
The UC Berkeley Forest Pathology and Mycology Laboratory does not provide a SOD testing service. For information on SOD testing please visit www.suddenoakdeath.org This activity possible thanks to funding from:
USDA Forest Service, State and Private Forestry
The Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation
Agdia, Inc. http://www.agdia.com
Disclaimer: Mention of any company, trade name, or commercial product does not constitute endorsement by the University of California or recommendation for use. |